Authored by: Humza Rana
Overview of Diabetes Management Innovations in the GCC Region
The rising global prevalence of diabetes calls for the integration of innovative technologies aimed at improving patient treatment outcomes, particularly in the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) region, which includes Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia (KSA), and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Diabetes currently affects approximately 537 million individuals worldwide, and the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) projects this number will grow to 643 million by 2030. Factors such as COVID-19 infections and mental health issues have increased the risk of developing diabetes, heightening the urgency for better diabetes management strategies and mitigation of related complications like retinopathy, foot ulcers, kidney disease, heart attacks, strokes, and ketoacidosis.
The worldwide incidence of diabetes is expected to rise by 59.7% from 2021 to 2050, increasing from 6.1% in 2021 to 9.8% by 2025. By 2025, approximately 1.31 billion individuals are expected to be living with diabetes. Current management approaches include glucose monitoring systems, hybrid closed-loop systems, and pharmacological or biologically based treatments. Innovations in these areas aim to enhance existing tools while also exploring new technological methods for preventing and managing diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D)
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the body’s immune system destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. It is often referred to as insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes. Those affected require daily insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels. In 2017, approximately 9 million people worldwide lived with Type 1 diabetes, mostly in high-income countries. Despite significant research, the causes of Type 1 diabetes remain unknown, and there are no established preventive measures.
Type 2 Diabetes (T2D)
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or the cells become resistant to it. This form of diabetes accounts for 90% of all diabetes cases. When unmanaged, it can result in severe health complications, including damage to blood vessels and nerves. Type 2 diabetes is often preventable through lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and maintaining a healthy weight. Risk factors also include genetics and environmental factors.
Glucose Monitoring Technology
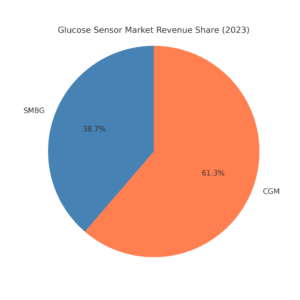
Efficient glucose monitoring is critical to managing both types of diabetes, particularly in people with Type 1 diabetes who rely on continuous monitoring for optimal care. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) are increasingly favored as they eliminate the need for frequent finger pricks. Most CGMs today use microneedle-based sensors that measure glucose in interstitial fluid (ISF), but there is also a growing interest in non-invasive technologies that provide an alternative to needle-based sensors.
Current non-invasive solutions tend to have lower accuracy compared to minimally invasive sensors, but they are expected to see improvements over the next two to three years. For example, Nemaura Medical’s sugar BEAT, a non-invasive wearable glucose monitor, was approved by the Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) in 2023. This approval has the potential to benefit the 4.27 million adults living with diabetes in Saudi Arabia, roughly 17.7% of the adult population.
In addition to enhancing accuracy, other important areas for advancement include the miniaturization of devices for better ease of use and growing consumer interest in over-the-counter devices. Industry leaders such as Dexcom, Abbott, Medtronic, and Senseonics dominate the CGM market, with Medtronic, Abbott, Dexcom, and Roche being particularly strong in the GCC region.
Significant emerging technologies from companies like Know Labs and Life Plus involve radiofrequency and optical sensing techniques for non-invasive glucose monitoring. While most non-invasive CGMs currently exhibit a Mean Absolute Relative Difference (MARD) exceeding 10%, future advancements are expected to improve accuracy, paving the way for these technologies to become viable solutions for Type 2 diabetes patients as well.
IDTechEx Analysis Highlights:
This IDTechEx analysis presents historical market insights and projections spanning ten years across four primary product categories through 2035.
The market for diabetes management devices has undergone significant transformations in the last ten years. Central to this evolution is the transition from electrochemical glucose test strips that necessitate finger pricking to minimally invasive continuous glucose monitors (CGMs). The multi-billion-dollar test strip sector has been on a gradual downturn since the 2010s, while CGM manufacturers have seen steady expansion. IDTechEx forecasts that by 2035, the yearly revenue from glucose test strips will constitute merely 5.15% of the overall diabetes management device market. IDTechEx predicts that the industry for diabetes care technologies will surpass US$44 billion by 2035, propelled by the expansion of continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and insulin pump sectors over the next decade.
Emerging Artificial Pancreatic Systems:
Hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery systems, often referred to as artificial pancreas, are becoming a pivotal solution for diabetes management, particularly for individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D). The artificial pancreas consists of three fundamental elements: continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), an insulin pump, and a digital device either internal or external for tracking blood glucose levels. Since 2021, the HealthPlus Diabetes and Endocrinology Centre in Abu Dhabi has been providing the Medtronic MiniMed 780G to those with type 1 diabetes.
Presently, some of the key hurdles in utilizing an artificial pancreas include the necessity for manual and intricate carbohydrate calculations, a limited glucose target range, and the demand for enhanced precision in the real-time measurement of insulin delivery flow and volume. Furthermore, there are very few artificial pancreas systems that have received regulatory approval. Emerging advancements in this field are tackling several significant challenges. For example, Beta Bionics has introduced the FDA-cleared iLet Bionic Pancreas, which eliminates the need for users to manually compute carbohydrate intake, requiring only a basic awareness of carbohydrates. Sequel MedTech’s FDA-cleared twist system ensures the precise measurement of each insulin dose administered. At present, only Insulet Corp offers FDA-approved tubeless insulin pumps, but additional companies, including Embecta and PharmaSens, are on the cusp of launching and commercializing tubeless insulin patch pumps to enhance user convenience.
Artificial pancreas systems are also being developed for individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D); firms such as Beta Bionics, Sequel MedTech, and Embecta are actively engaged in this endeavor. Emerging innovations featuring all-in-one modular bionic pancreas devices hold the potential to significantly transform diabetes care worldwide over the long term.
Disruptive Insulin Delivery Technologies:
Administering multiple insulin injections throughout the day can be quite uncomfortable, necessitating frequent changes of the insulin injection site for optimal absorption. This can negatively affect adherence among patients. Microneedle insulin delivery systems and insulin pumps may not receive full insurance coverage, resulting in higher out-of-pocket expenses for those living with diabetes. New advancements in insulin administration are addressing these issues, leading to the creation of intelligent insulin pens and pumps that enhance glycaemic control and lessen discomfort compared to traditional syringe methods.
Innovative products like connected smart insulin pens, patch-based tubeless insulin pumps, implantable insulin delivery systems, and insulin jet injectors are poised to revolutionize insulin administration techniques. Notably, in 2023, Gulf Drug introduced the EOPatch, a wearable insulin pump from EOFlow, in the UAE. Gulf Drug is also gearing up for the rollout of EOFlow in additional GCC nations, including Saudi Arabia, which will facilitate precise diabetes management in the region.
There is an increasing interest in creating oral or inhalation-based insulin options to improve adherence to diabetes treatment. MannKind Corporation’s Afrezza stands as the sole FDA-approved inhalable insulin formulation currently on the market. Companies like Oramed and Biocon are developing oral insulin products currently undergoing Phase 2-3 clinical trials, paving the way for potential launches of oral insulin formulations in the coming years to enhance diabetes management and patient adherence.
Challenges:
Type 2 diabetes-related costs to the NHS are projected to reach £17 billion by 2035, presenting a significant public health challenge. This economic strain underscores the urgent need for effective prevention and management strategies. Despite the increasing prevalence of pre-diabetes, there remains a lack of targeted disease intervention programs to prevent its progression to type 2 diabetes. Enhancing medication adherence is critical, as non-adherence contributes to poor glycemic control and increased complications. Expanding access and ensuring comprehensive coverage for diabetes-related medications and essential supplies, such as glucose monitors and insulin, are also pivotal. Addressing these gaps through public health policies, innovative solutions, and patient education could reduce the long-term burden on the NHS while improving outcomes for individuals at risk or living with diabetes.
Moving Forward:
In the upcoming years, there will be an increase in partnerships between insulin delivery firms and CGM specialists to create hybrid closed-loop systems aimed at enhancing diabetes care. Additionally, there will be a rise in collaborations between devices and software to bolster automation in artificial pancreas setups and automated diabetes management. With the ongoing surge in mobile device usage and internet access across the GCC regions, health technology applications will broaden to encompass innovations focused on the prevention and management of lifestyle-related conditions like diabetes.
For example, algorithms like Tidepool Loop and Diabeloop are expected to see greater implementation for automating diabetes care in the future. Control-IQ (Tandem Diabetes Care) is an FDA-approved advanced hybrid closed-loop algorithm integrated into the Tandem t:slim X2 insulin pump. Predictive technology manages both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. Smart Guard (Medtronic) is an algorithm in Medtronic’s insulin pumps, such as the MiniMed 670G and 780G series. The embrace of such technologies will also assist in alleviating the negative effects of escalating healthcare costs in the GCC, which are driven by the growing prevalence of obesity and diabetes in the region.
Moreover, there is a consistent increase in global investments in diabetes management technologies. Biolinq secured US$58 million in 2024 to propel its intradermal glucose sensor through clinical research. In 2023, Persperion obtained US$4 million to support the R&D of sweat-based glucose sensors. This surge in funding will foster the development of innovative user-driven technologies for precise diabetes management going forward. Noninvasive glucose sensors, compact artificial pancreas systems, and oral insulin formulations are poised to be essential growth avenues in connected diabetes care.
Conclusion:
Diabetes remains a critical global health concern, affecting millions worldwide and placing a significant burden on healthcare systems. However, recent strides in raising funds to develop artificial pancreatic systems are offering hope for better management and control of diabetes. These advanced systems, powered by cutting-edge algorithms, are making remarkable progress. Solutions such as Tidepool Loop, Diabetic Loop, and Control-IQ (Tandem Diabetes Care) are pioneering efforts in harnessing technology to optimize insulin delivery, improving quality of life for diabetic patients. These innovations are a testament to how collaborative efforts, combined with technology and algorithm development, can revolutionize diabetes care. As research and funding continue to grow, these systems are poised to play a transformative role in the management of diabetes, ensuring a future where better control and improved health outcomes are within reach for individuals globally.
Q/A:
- What are the highlights raised by this article?
A) It’s about the diabetic management system. Its main focus is to create an artificial pancreatic system that helps humans maintain diabetes. It also highlights the raising funds needed to improve the diabetes management system. 537 million individuals aged 20 to 79 are affected by diabetes, and the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) forecasts that this figure will surge to 643 million globally by 2030. - What is GCC?
A) The GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) comprises six Arabian countries: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, KSA, and UAE. - What is CGM & SGBM?
A) Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Technology is a healthcare tool that delivers instant, ongoing observation of glucose (sugar) levels in individuals with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes (T1D). It presents a more sophisticated and minimally invasive option compared to conventional finger stick testing, which usually requires pricking the finger several times daily to collect a blood sample for glucose assessment. SGBM stands for Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose. - What is NHS?
A) The NHS represents the National Health Service, the publicly financed healthcare system in the UK. It was founded in 1948 with the intention of delivering health services that are costless at the time of access, supported by taxes.
Sources:
- IDTechEx Diabetes Management Market
- NHS Diabetes Prevention Program Evaluation
- GCC Diabetes Care Devices Market
- IDTechEx Continuous Glucose Monitoring